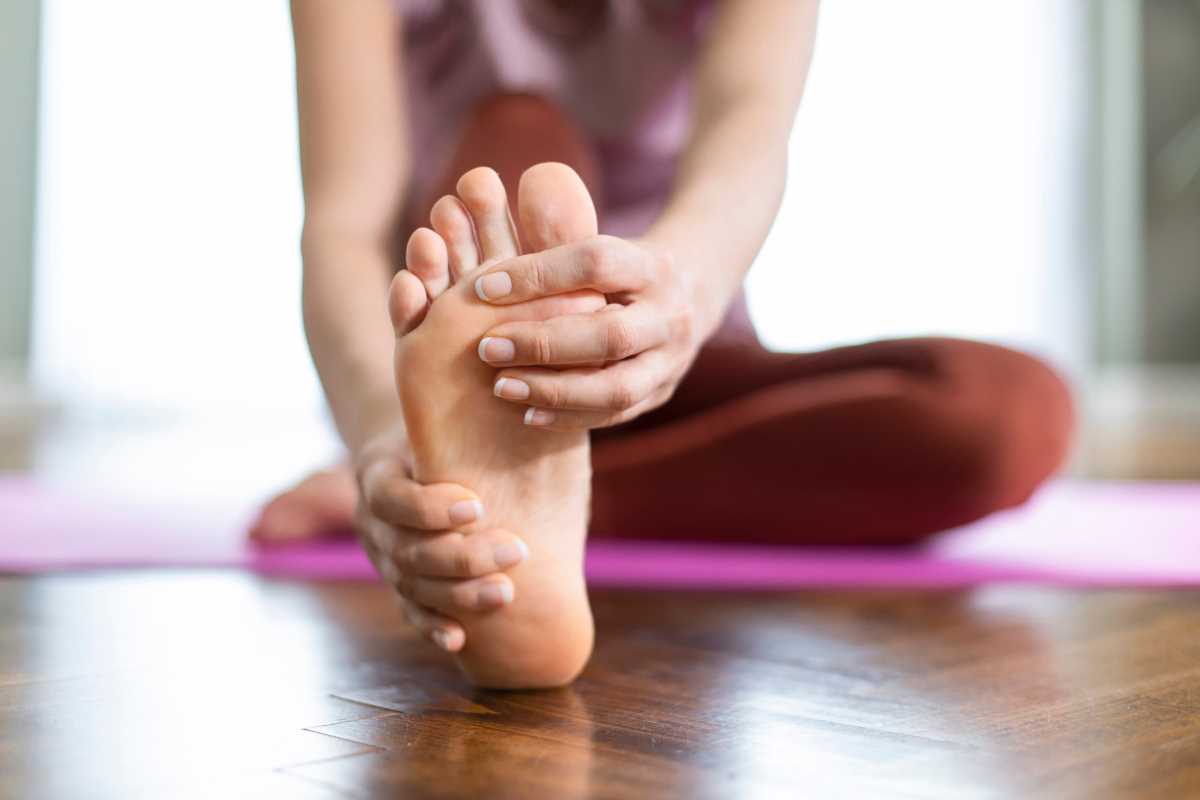
Daily joint pain often disrupts routines and makes even simple tasks more difficult. Relief is possible when you focus on solutions that ease stiffness and reduce inflammation. You can take steps to restore comfort and flexibility, allowing you to return to activities you enjoy. This guide shares seven effective approaches that help manage pain and support joint health, all without the need for surgical procedures. Whether your discomfort stems from aging, overuse, or an old injury, these practical tips can help you move with greater ease and confidence every day.
What Causes Chronic Joint Pain
- Persistent aching or soreness in one or multiple joints
- Stiffness in the morning or after periods of rest
- Swelling, warmth, or redness around certain joints
- Limited range of motion and occasional instability
Joint pain occurs when cartilage breaks down or when inflammation impacts the lining of the joint. Injuries, repetitive motions, or underlying conditions like arthritis can trigger that inflammation. Recognizing what causes your discomfort helps you choose methods that address the root problem instead of masking symptoms.
Method 1: Physical Therapy and Exercise
- Strength Training: Focus on low-impact moves such as seated leg presses or light dumbbell routines to build muscle without stressing joints.
- Range-of-Motion Exercises: Perform gentle circles or side-to-side movements to maintain flexibility in your ankles, wrists, and shoulders.
- Balance Drills: Stand on one foot or use a wobble board to improve stability around knees and ankles, reducing the risk of falls.
- Aquatic Workouts: Move in warm water to support your body weight while you stretch and strengthen.
- Stretching Routine: Hold stretches for 20–30 seconds, targeting hamstrings, calves, and hip flexors to ease tension around knee joints.
Physical therapists can tailor exercises to match your current abilities. They’ll adjust movements so you feel challenge but avoid sharp pain. Practicing these exercises three times a week often brings noticeable relief within a month.
Method 2: Weight Management and Nutrition
Extra pounds add strain to weight-bearing joints, especially hips, knees, and ankles. Shedding even a few pounds redistributes pressure and cuts pain significantly. Combine a balanced diet rich in lean protein, whole grains, vegetables, and healthy fats with portion control to achieve gradual, sustainable weight loss.
Anti-inflammatory foods can calm flare-ups. Fatty fish such as salmon, walnuts, and flaxseed deliver omega-3s that curb inflammation. Berries and leafy greens pack antioxidants that protect joint tissue. Swap processed snacks for fresh fruit, and season meals with turmeric or ginger to add natural inflammation support.
Method 3: Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat increases blood flow and loosens stiff muscles around a painful joint. Use a warm towel or heating pad for 15–20 minutes before activity to prepare the joint for movement. After exercise or during a flare-up, cold therapy can halt swelling. Wrap ice packs in a cloth and rest them over the joint for up to 10 minutes at a time.
Alternate between heat and cold if stiffness and swelling both occur. Start with heat to relax tissue, follow with cold to reduce any inflammation, and repeat this cycle a few times. Many people find relief when they establish this routine twice a day.
Method 4: Mind-Body Techniques
- Breathing Exercises: Deep, slow breaths can lower tension and reduce pain signals to the brain.
- Yoga for Joint Health: Gentle poses like child’s pose or seated twists improve flexibility without jarring impact.
- Guided Imagery: Visualize cool waves washing over an inflamed knee or shoulder to distract pain perception.
- Biofeedback: Use simple home devices that measure muscle tension and help you learn how to relax muscles with guided cues.
These techniques work together to calm the nervous system and ease muscle tightness. Practicing for just 10 minutes a day builds resilience against pain flares over time.
Method 5: Assistive Devices and Supportive Gear
Braces, wraps, and orthotic shoe inserts can change joint alignment and reduce stress during daily activities. For example, a neoprene knee sleeve offers gentle compression while you walk, boosting confidence and stability. You might try *TheraBand* elastic bands to support weakened wrists or ankles during light tasks.
Using a cane or walking stick distributes weight away from an injured joint. Choose a device at a height that keeps your elbow at a 20-degree bend. Simple changes like wearing shock-absorbent shoes or raising chairs to a comfortable seat height also protect joints over the long term.
Method 6: Lifestyle Changes and Ergonomics
Rearrange your home and workspace to reduce repetitive strain. Place everyday items between waist and shoulder height to avoid bending or reaching. Use a cushioned mat if you stand for hours, and switch tasks to prevent overworking the same joints.
Sleep positions influence joint comfort too. Use pillows to align hips and knees when you lie on your side or place a small pillow under your knees if you sleep on your back. A mattress with medium-firm support helps maintain healthy spinal curves and minimizes joint pressure.
Method 7: Natural Supplements and Topical Solutions
Some supplements contain compounds that support joint tissue. *Glucosamine* and *chondroitin* interact with cartilage repair processes, though results vary between individuals. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement plan.
Topical creams containing capsaicin, menthol, or camphor offer a cooling or warming sensation that distracts from pain signals. Gently massage the cream into the skin around the joint. Reapply based on the product’s instructions to maintain relief throughout the day.
Trying different approaches can help you find relief and improve joint health. Combining methods allows you to better manage your pain daily.
 (Image via
(Image via